What is a GPX file: and how you can get the most out of it
Our expert guide to GPX files covers what they are and how they can enhance your experience when planning, carrying out and looking back at your adventures

All the latest inspiration, tips and guides to help you plan your next Advnture!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The London Mountaineering Club has a running challenge that involves tagging all of Wales' highest 15 mountains in a single outing, with the aim of completing it in under 24 hours. The route and the order of the peaks isn't fixed, as long as all 15 summits are visited, you can go whichever way you want.
Back in the day, members would pore over the huge topographical map on the wall of the club's hut, tracing lines and discussing the optimum way to achieve the feat. These days, all you have to do is seek out someone who's done it quickly and ask for their GPX file. Easier still, pop their name into komoot or Strava and you can see their GPX plot, download it and upload to your own phone or Garmin watch.
So, what is a GPX file? How can these magical bits of computer code assist you on your adventures and how can you get the most out of them? Our Mountain Leader and digital navigation expert is here to decipher the code.
What is a GPX file?
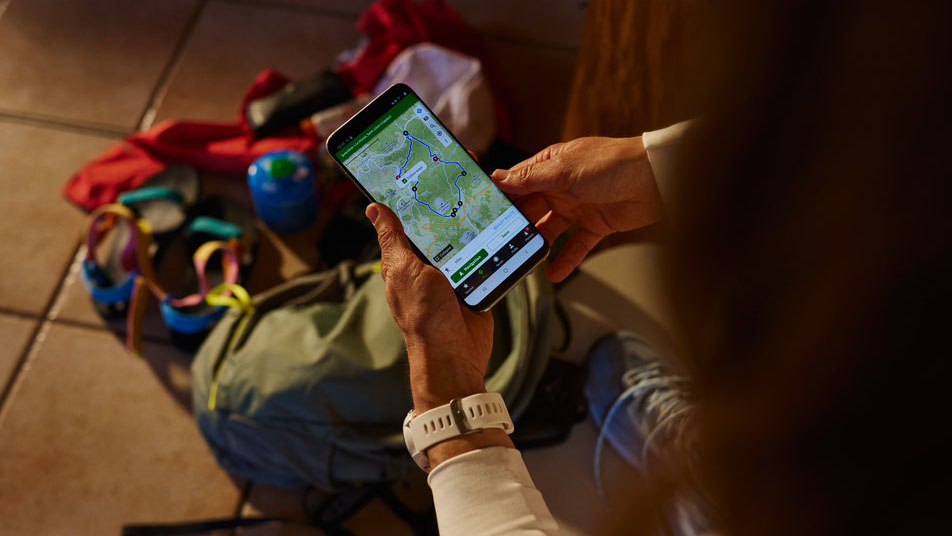
GPX files contain GPS (Global Positioning System) data that can be read and used by applications, GPS units, computer software and on the web to display a route on a map. They can be used when planning a route, or as a navigational aid while out in the backcountry, or to show off your adventures in digital map form afterwards.
GPX stands for GPS Exchange Format file. If you open a raw GPX file, you will see lots of lines of code – written in a coding language known as xml – full of GPS coordinates and data points.
The code of a GPX file always consists of waypoints, routes and tracks. These geographic data points apply to a location. Other information such as time, elevation and heart rate can also be ascribed to them, depending on what application you are using to create the file. This is how Strava knows how fast your were going at a certain point in your run, or how AllTrails knows what your elevation was halfway through your hike. It's all captured in the code.
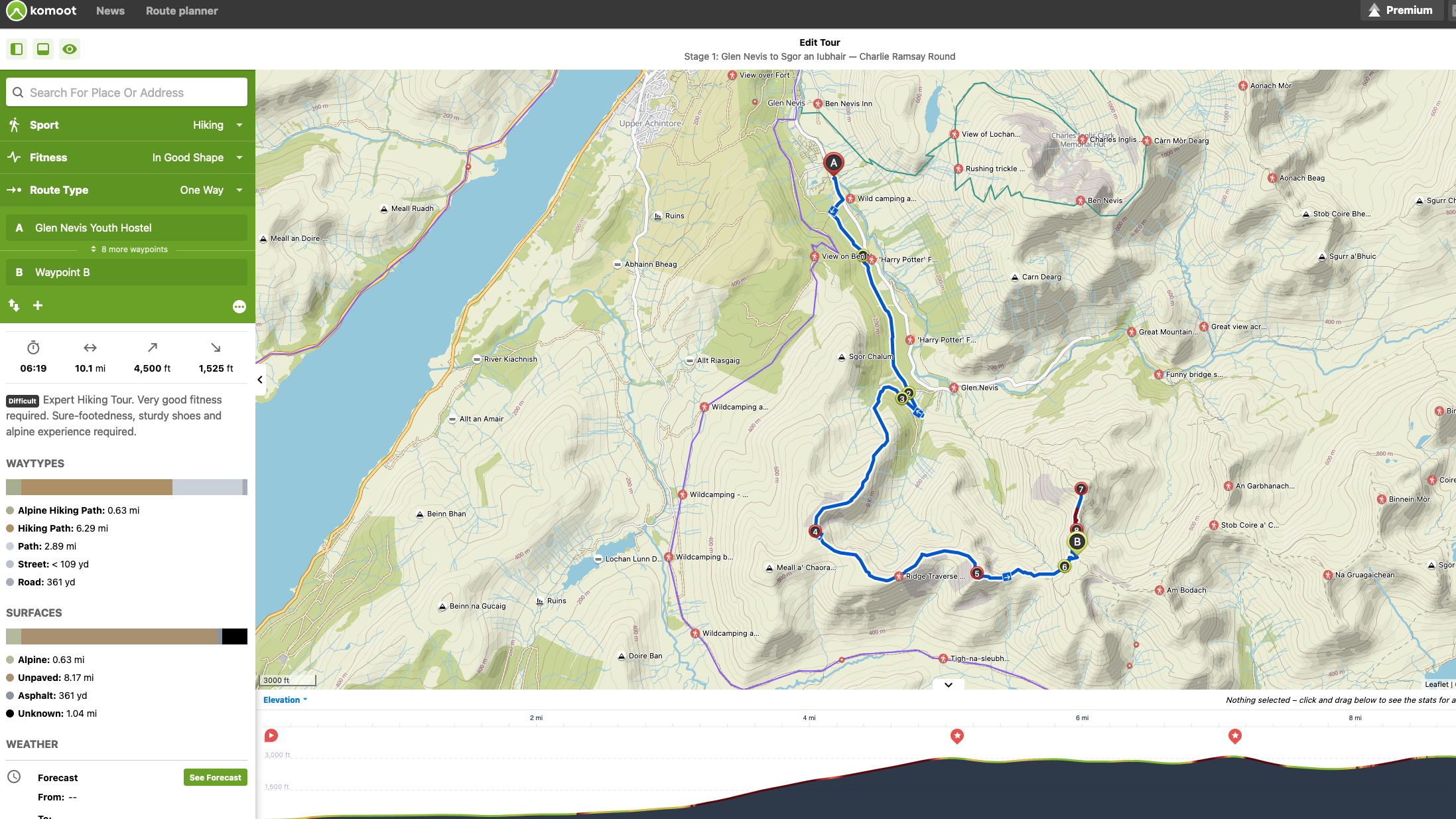
However, to use GPX files practically, you don’t need to be clued up on the intricacies of the code. You are much more likely to open a GPX file with mapping applications, where you will see a plotted route across the map along with other statistics and visuals, depending on the platform.
All the latest inspiration, tips and guides to help you plan your next Advnture!
Meet the expert

Alex is a qualified Mountain Leader who advocates both the use of traditional navigation with a map and compass, and the use of digital navigation aids, like smartwatches and apps. He does a substantial amount of work with the route planning, navigation and adventure sharing platform komoot, using GPX files on a daily basis.
How times have changed
- You can use planning apps to estimate how long your hike will take, what surfaces you'll encounter and how strenuous it will be

Times have changed. At the planning stage, you can now plot your intended route on digital mapping applications that will estimate how long your trek will take, what kind of terrain your hiking boots can expect to meet and how strenuous it will be. Once on the trail, you can track your location accurately using a GPS (Global Positioning System) unit or your phone (for more on these, check our out best GPS watches and best navigation apps). Afterwards, you can use the data gathered to analyse your performance, with information about almost everything at your fingertips, from elevation change to calories burnt.
It may not be as romantic as the traditional approach to an adventure, but this technology is making the outdoors more accessible to more people, and it’s here to stay. For many, a GPS application is a bona fide hiking essential. Crucial to this shift are GPX files.
How can GPX files be used?
- You can download GPX files and edit the routes for your own purposes using a navigation app
- You can use the raw or edited routes to aid your navigation while on the trail
- You can create GPX files from the activities you complete and share them with your followers
GPX is the gold standard file type for GPS navigation. It is used by almost everyone who manufactures GPS units (such as Garmin and Suunto), as well as hundreds, if not thousands, of web and phone applications (such as Google Earth, Google Maps, car navigation systems, camping apps and outdoor applications like komoot, Alltrails and Strava).
You’ve undoubtedly created GPX files many times without knowing it. If you’ve been for a run or a hike and recorded your route using your phone, GPS device or smartwatch, you’ve created a GPX file. Apps like Garmin Connect, komoot and Strava provide a visual representation of the data for you to analyse and enjoy afterwards.

If I'm visiting a new region and I fancy going for a trail run, for example, I can look online or on komoot to see if anyone has shared one in the past. That way, I can download their GPX file and use it for my own purposes.
Alex Foxfield, Mountain Leader
Some applications allow you to download the GPX file of your completed adventure so that you can share it with your friends, or even the world. If there’s a thru-hiking route or a circular hike you’ve been eyeing up for a while, the odds are that someone has already shared the GPX file on the internet. Better still, you can take their file and edit it for your own purposes.
This is because the best navigation apps today, such as the popular komoot, not only create a GPX file from your completed activities but also provide tools that allow you to plan a backpacking adventure on a digital map. By creating waypoints and plotting your route, you create a new GPX file, which you can return to and edit as many times as you please before the adventure.

Finally, once you’re on the adventure, you can use a GPS device or app to track your location against your plotted route. If you lose the trail, many GPS apps and units will recalculate the best route to get you back on track, just like when you’re driving and you deviate from your SatNav’s planned route. Some can even provide SatNav style voice instruction, although to be honest being told repeatedly to “do a U-turn!” just because I’ve gone to check out a hidden waterfall that was off my planned route can be a little bit irritating.
However, as with most trail tech, the benefits of GPX files outweigh the negatives, changing the way we plan, explore and reflect on our time in the great outdoors.
Alex is a freelance adventure writer and mountain leader with an insatiable passion for the mountains. A Cumbrian born and bred, his native English Lake District has a special place in his heart, though he is at least equally happy in North Wales, the Scottish Highlands or the European Alps. Through his hiking, mountaineering, climbing and trail running adventures, Alex aims to inspire others to get outdoors. He's the former President of the London Mountaineering Club, is training to become a winter mountain leader, looking to finally finish bagging all the Wainwright fells of the Lake District and is always keen to head to the 4,000-meter peaks of the Alps. www.alexfoxfield.com

